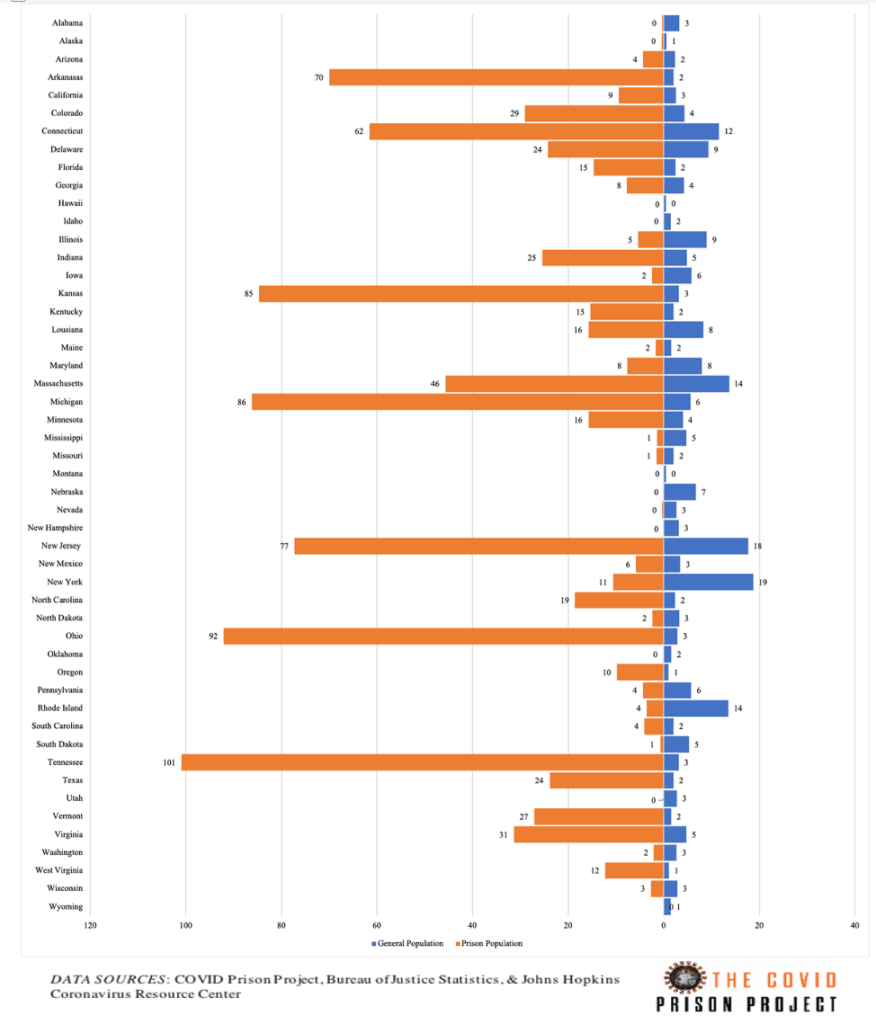
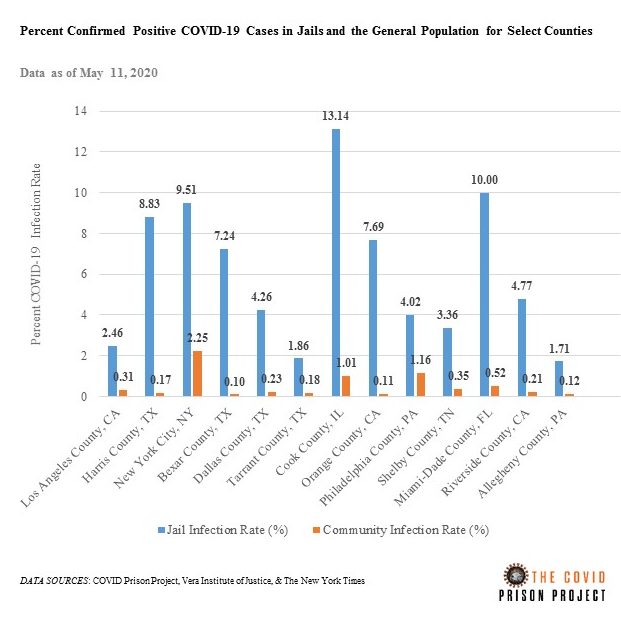
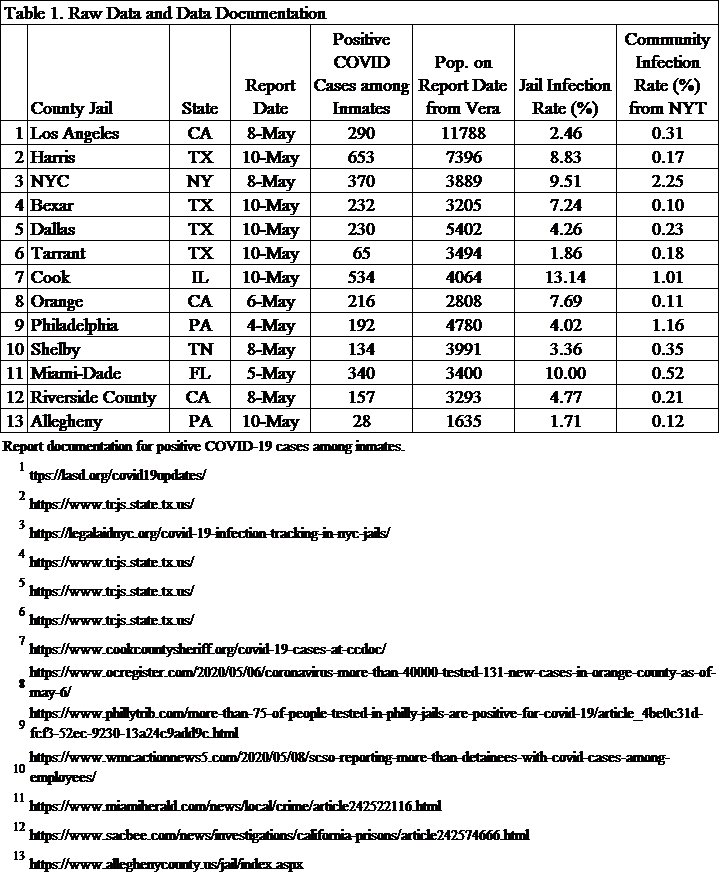
Among the 53 prison systems that provide source data for the COVID Prison Project, 6 designate which of their facilities are public or private. We analyzed some of these data to get understand if there are differences in testing practices, and, subsequently, case rates in private and public facilities.
We found that private prisons have fallen behind their public counterparts in COVID testing and case detection. Among federal prisons, 6 out of the reported 11 private prisons are not reporting any COVID data (Big Spring FL, Big Spring, Dalby, Moshannon Valley, Reeves CI, Reeves DC). The five prisons reporting COVID data only report the number of inmates that have tested positive for COVID. As of June 8th, these private facilities have only reported a total of 72 positive cases and no testing information. This number has remained constant at 72 since reporting began on May 8th.
In Florida, private prisons have been slower to ramp up COVID testing than public facilities with three of the state’s five private prisons (Graceville, Lake City, Moore Haven) having tested fewer than 10 people who are incarcerated as of June 3, 2020. The state’s two private prisons that have detected COVID outbreaks are, unsurprisingly, the two that have tested over 1,200 inmates each (Gasden, South Bay). However, comparisons between Florida’s public and private facilities remain difficult, as certain private (South Bay) and public (Liberty) facilities that have detected COVID outbreaks are reporting a decreasing cumulative number of COVID tests, which technically should be impossible.
Among other states reporting testing data and information relevant to which facilities are private, Hawaii’s private prison has only tested three inmate and West Virginia one inmate as of June 8th. In Hawaii, though, testing numbers are low for all facilities (regardless of private vs. public designation).
While Georgia does not report the total number of tests, as of June 8th, no private facilities in Georgia had reported a change in the number of positive or recovered cases since May 4th whereas public facilities are reporting increasing numbers almost daily. In addition, Georgia’s private facilities are not reporting any staff information while the public facilities are.
We are able to glean more information from Arizona, where the total number of people in each facility is reported. As of June 3rd, private prisons have tested 0.68% of inmates whereas public prisons have tested 4.63%. Of those tested, private prisons have found 21% of inmates to be positive and public prisons have found 12% to be positive, indicating a dire need for further testing.
In summary, we are still learning more about private facilities, and while many states do not report which facilities are private, where information is available, private facilities are, in many cases, testing less, waiting longer to enact robust testing measures, and are reporting fewer cases even when reporting higher rates of test positivity.